Abstract
Introduction: The ENDEAVOR study showed a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) for carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Kd56) compared with bortezomib and dexamethasone (Vd) in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) (Lancet Oncol . 2016;17:27-38). The PFS benefit with Kd56 vs Vd was seen regardless of the number of lines of prior therapy and prior treatment with bortezomib (BTZ) (Leukemia . 2017;31:115-122). In the overall survival (OS) analysis of ENDEAVOR, median OS was significantly longer for patients who received Kd56 than for patients who received Vd (47.6 vs 40.0 months; hazard ratio [HR] for Kd vs Vd, 0.79; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.65, 0.96; 1-sided P= 0.0100). Here, we present OS and safety analyses comparing Kd56 with Vd according to prior lines of therapy and previous exposure to BTZ.
Methods : Patients with RRMM who had received 1-3 prior lines of therapy were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive Kd56 or Vd. Prespecified stratification factors included number of prior lines of therapy and prior BTZ therapy (yes vs no). Patients in the Kd56 arm received carfilzomib as a 30-minute intravenous (IV) infusion on days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16 (20 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of cycle 1; 56 mg/m2 thereafter) and oral or IV dexamethasone (20 mg) on days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, 16, 22, and 23 on a 28-day cycle. Vd-treated patients received BTZ (1.3 mg/m2) given either IV or subcutaneously on days 1, 4, 8, and 11, and dexamethasone (20 mg) on days 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 11, and 12 on a 21-day cycle. Patients continued treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. An unstratified log-rank test was used to compare OS between treatment arms for each subgroup. The Kaplan-Meier OS rate and median OS time were estimated up to the time point where there were 10 or fewer patients (Kd56 and Vd combined) in the risk set. The study was not powered to detect differences in OS between subgroups. Adverse events (AEs) were presented as preferred terms and were not adjusted for exposure.
Results :A total of 929 patients were randomized to receive Kd56 (n = 464) or Vd (n = 465). The proportion of patients with 1 (Kd56, 49.8%; Vd, 49.2%) or 2-3 (Kd56, 50.2%; Vd, 50.8%) prior lines of therapy was balanced between the treatment arms. The proportion of patients with prior exposure to BTZ was also balanced between the Kd56 and Vd arms (54% in each arm) and within the subgroups of patients with 1 prior line (Kd56, 42.0%; Vd, 42.8%) and 2-3 prior lines of therapy (Kd56, 65.7%; Vd, 65.3%).
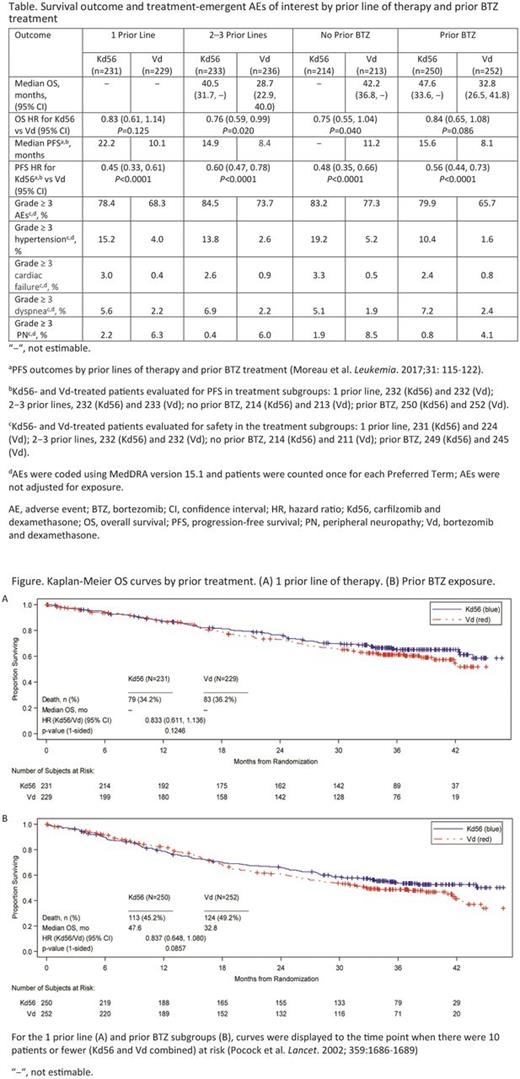
OS outcome and Kaplan-Meier OS curves by prior treatment are shown (Table and Figures). The risk of death was low in patients at first relapse, and it was not possible to reliably estimate median OS for the Kd56 and Vd arms in the 1 prior line subgroup (Figure A). The HR of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.61, 1.14) suggested a survival advantage for Kd56 vs Vd for patients at first relapse. For patients with 2-3 prior lines of therapy, Kd56 improved survival by 11.8 months vs Vd (median OS for Kd56 vs Vd, 40.5 vs 28.7 months; HR 0.76; 95% CI: 0.59, 0.99). For patients without prior BTZ exposure, the median OS was not reached in the Kd56 arm and was 42.2 months in the Vd arm (HR 0.75; 95% CI: 0.55, 1.04); for patients with prior BTZ exposure (Figure B), the median OS was 47.6 months vs 32.8 months (HR 0.84; 95% CI: 0.65, 1.08).
The frequency of grade ≥ 3 AEs was 78.4% (Kd56) and 68.3% (Vd) in the 1 prior line subgroup, and 84.5% (Kd56) and 73.7% (Vd) in the 2-3 prior line subgroup (Table). Grade ≥ 3 AEs were reported in 83.2% (Kd56) and 77.3% (Vd) of patients with no prior BTZ exposure, and 79.9% (Kd56) and 65.7% (Vd) of patients with prior BTZ exposure (Table). The rates of grade ≥ 3 AEs of interest in the prior treatment subgroups in this OS analysis are presented (Table).
Conclusions :Treatment with Kd56 showed a survival benefit compared with Vd in patients with RRMM irrespective of the number of prior lines of therapy and previous exposure to BTZ. Kd56 extended PFS by 12.1 months and 6.5 months in patients at first relapse and in patients with 2-3 prior lines of therapy, respectively, and reduced the risk of death by 17% (1 prior line) and 24% (2-3 prior lines). Kd56 prolonged PFS by 7.5 months and OS by 14.8 months vs retreatment with BTZ in proteasome inhibitor-sensitive patients. In general, treatment was well tolerated. The rate of AEs in this subgroup analysis was consistent with that reported in the overall population. Moreover, no unexpected safety events occurred during longer follow-up.
Weisel: Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Siegel: Celgene, Takeda, Amgen Inc, Novartis and BMS: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Consultancy. San Miguel: Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MSD: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hájek: Amgen, Takeda, BMS, Celgene, Novartis, Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharma MAR: Consultancy, Honoraria. Ho: Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Novartis, Janssen, Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gaidano: Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria. Orlowski: BioTheryX: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Zhou: Amgen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kimball: Amgen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Moreau: Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene, Janssen, Takeda, Novartis, Amgen, Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Millennium: Consultancy, Honoraria; Onyx Pharmaceutical: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal